Ammonia (NH3) has played a crucial role over the last century in the production of urea, nitrogen-based fertilizers, and various other nitrogen-based compounds. Traditionally tied to the energy industry due to its productionʼs reliance on fossil fuels, ammonia is now at the forefront of discussions about
decarbonization. Particularly, renewable ammonia is in light of the European Union’s decarbonization goals and the push for a renewable hydrogen industry. The two main topics on this subject are decarbonizing traditional ammonia applications and exploring its potential direct use as a Renewable Fuel of Non-Biological Origin (RFNBO).
Despite its production largely relying on grey hydrogen, ammonia was not a common topic in decarbonization discussions until recently. The production of this essential product for the global food supply has been acquainted with 2% of global energy consumption and 1.3% of the total CO2 emissions. Additionally, in a global economy based primarily on renewable energy, ammonia has been reported as a key component for offshore energy transportation and a future sustainable fuel.
A modern commodity
The modern history of ammonia can be traced back to the beginning of the 20th century, with the development of the Haber-Bosch process by Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch. If you have read something about ammonia production before, you are certainly at least familiar with this name. We will not get deeper into it, but it is important to highlight its relevance, as this process was the key to the beginning of a chemical revolution that enabled the massive production of ammonia, synthetic fertilizers, and an explosive population growth from two to over seven billion inhabitants in less than a century, due to the increase in food production worldwide.
Nowadays, all mineral nitrogen fertilizers are produced based on ammonia and its derivatives, which corresponds to nearly 70% of the total ammonia global demand. Hence, its production is still a fundamental component of something as basic as food production. The other 30% is used for different purposes such as the production of plastics, explosives, and synthetic fibers. In Figure 1, the diagram shows a mass flow in the ammonia supply chain from 2018, including the composition of fossil fuel consumption, and the final products as fertilizers.
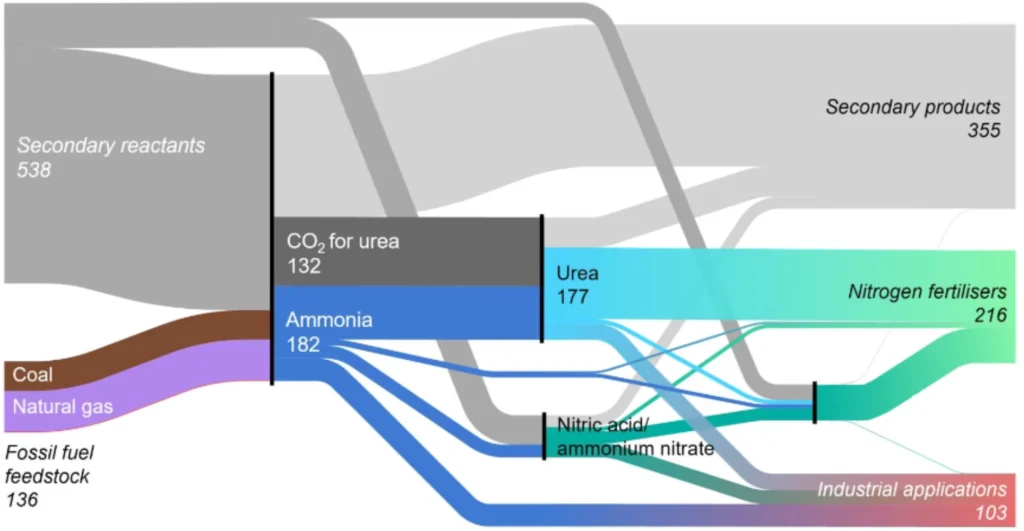
Mass flow in the ammonia supply chain from fossil fuel feedstocks to nitrogen fertilizers and industrial products. The original chart was created by Levi and Cullen.
The thickness of the lines in the diagram above is proportional to the magnitude of the mass flows. All numeric values are in million tonnes per year of production using production data for 2019. Only the fossil fuel quantities consumed as feedstock are shown; the diagram does not represent process energy inputs.
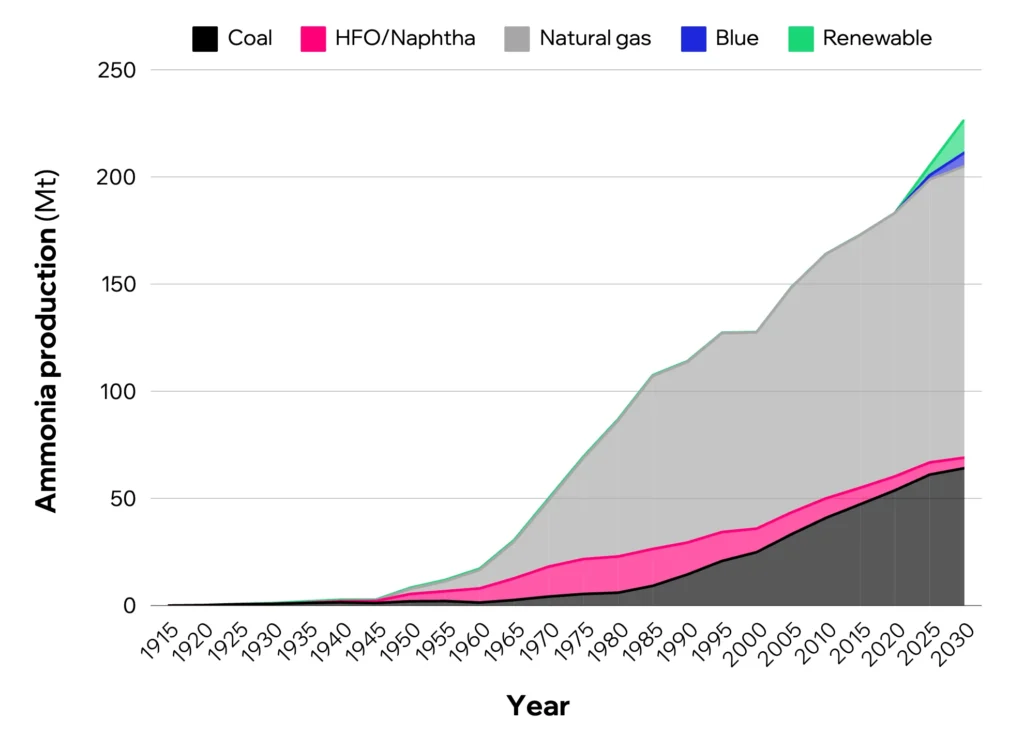
In 2019 global ammonia production reached approximately 185[Mt], with a growing rate of 2.3% per year. In Figure 2, the chart shows the total amount of ammonia produced per year since 1915, and the projections until 2030. It should be noted that most of its production has been based on fossil fuels, the use of natural gas being the most common method in the last 60 years.
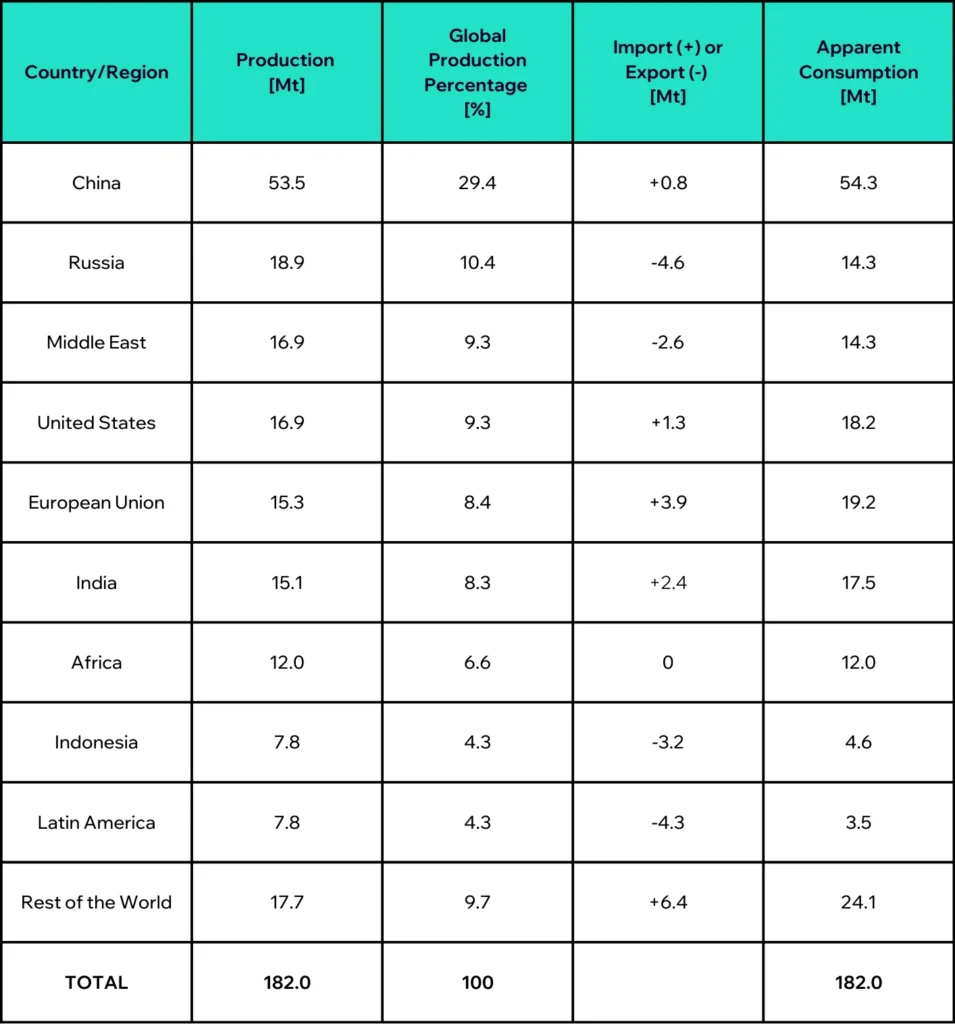
Many countries manufacture ammonia within their borders, but international trading is also common. Countries rich in fossil fuel resources enjoy a competitive edge due to lower production costs when they have a well established ammonia industry. Consequently, some nations can export it as well. Table 1 presents the production and apparent consumption volume of
ammonia in several countries or regions.
Ammonia CO2 footprint
While the Haber-Bosch process has undergone substantial optimization over the years, with a focus on increasing product purity and production efficiency, its CO2 footprint has historically been overlooked. Nowadays, current production methods result in the release of around 2.4 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of ammonia, making it one of the most emission-intensive commodities produced by heavy industry.
When we compare its direct emissions (Figure 3), these are over 70% more intensive than crude steel production, and four times that of cement.
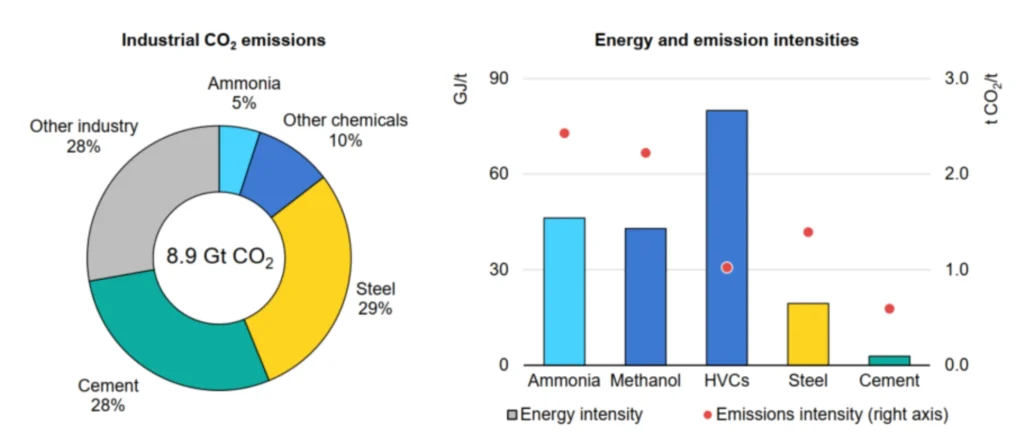
- Energy intensities are shown on a gross basis to facilitate comparison between products and sectors.
- Industrial energy consumption includes energy used in blast furnaces, coke ovens, and chemical feedstock. Industrial CO2 emissions include process emissions.
- HVCs = high-value chemicals. including ethylene, propylene, benzene, toluene, and mixed xylenes.
New opportunities for renewable ammonia
Renewable ammonia has generated major attention from governments and the private sector in the last few years. Comparatively, when it is produced with renewable hydrogen and an electrically driven Haber-Bosch process, it has a significant reduction in its CO2 footprint. Depending on the renewable energy source, one tonne of green ammonia may liberate 0.38 to 0.53 tonnes of CO2, implying a reduction in its emissions of almost 80%.
Based on this new approach, and the integration of carbon capture technologies, promising future scenarios are being considered to reduce the environmental impact of this fundamental component for the modern world.
Figure 4, shows the possible future scenarios for conventional and renewable ammonia production in the next 30 years, regarding CO2 emissions and the expected energy consumption. These projections require a considerable transition into electrolysis-produced ammonia, to achieve the goal of 2050 carbon neutrality.
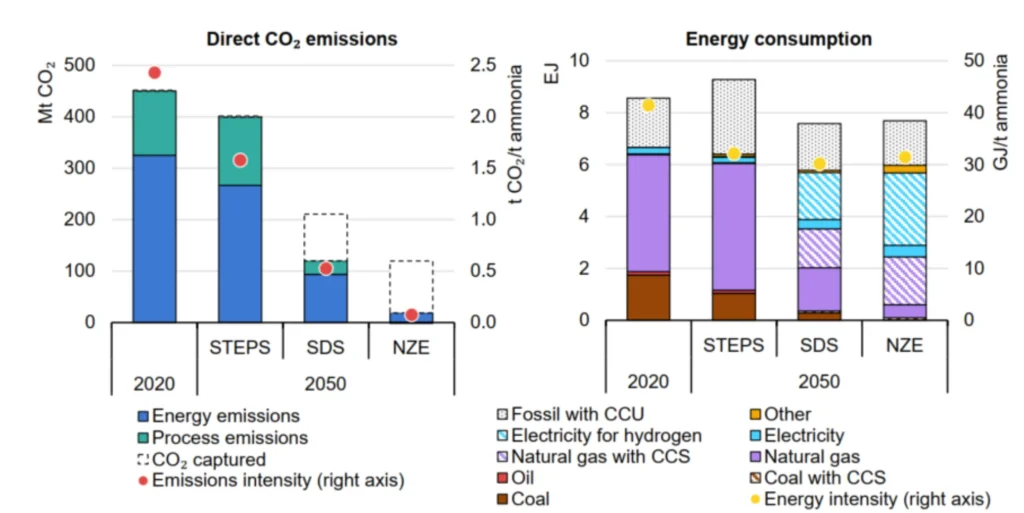
by scenario.
Ammonia used as an energy carrier is not included. Energy consumption includes that used as feedstock. Energy intensities are shown on a net basis.
- STEPS = Stated Policies Scenario.
- SDS = Sustainable Development Scenario.
- NZE = Net Zero Emissions by 2050.
- CCU = Carbon capture and utilisation.
- CCS = Carbon capture and storage.
- “Other” is comprised mostly of Bioenergy, as well as a small amount of hydrogen-based synthetic methane imported via blending in the natural gas grid.
The energy industry has been through a continuous evolutionary process for the last 20 years, looking up for a greener future. One of the latest trends, with a high game-changer potential, is the integration of ammonia as a sustainable energy carrier.
Since pure hydrogen transportation and storage present several drawbacks, chemical hydrogen carriers are an attractive alternative. These are molecules that contain a high concentration of hydrogen per unit of mass and volume. Among these, ammonia has gained important traction lately, especially for long-distance shipping. Since it can be transported at 25°C and at comparatively low pressure (10-20 bar), it is a cheaper and simpler transport alternative for certain applications.
Considerable research has been done regarding the best alternatives for hydrogen transportation and storage, including technical and economic aspects. It has been shown that the Levelised Cost of Transport for hydrogen as gas, would be cheaper through specially conditioned pipelines. However,
for off-shore commercial activities, ammonia has a substantially reduced levelized cost of transportation compared to other alternatives.
Figure 5 depicts the transportation cost of hydrogen as a gas through different types of pipelines (left), with the alternatives through shipping (right) using liquified H2 (LH2), ammonia, and other Liquified organic Hydrogen carriers (LOHC). From these charts, we can understand that for offshore transactions, NH3 would be the most competitive alternative.
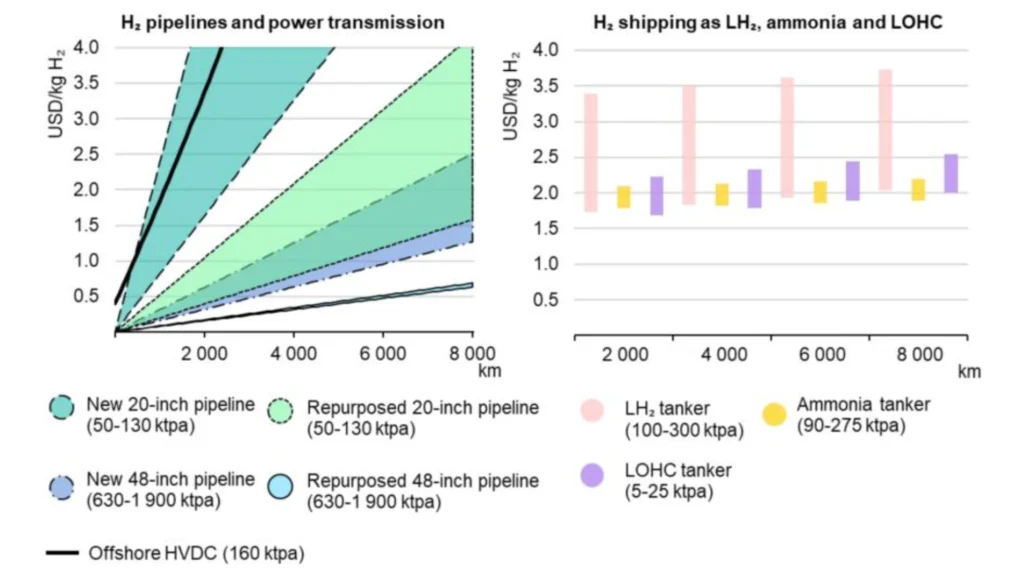
NZE Scenario, 2030.
HVDC: high-voltage direct current; ktpa: kilotonnes per year; Hydrogen pipelines refer to onshore transmission pipelines operating at 25-75% of their design capacity for 5.000 full-load hours. Electricity transmission by offshore HVDC indicates electricity transmission required to obtain 1 kg H2 in an electrolyzer with 69% efficiency.
Transport costs by ship include investment and operational costs to convert hydrogen to a higher-density carrier, store it, ship it, and reconvert it to deliver gaseous hydrogen.
The shipping capacity range corresponds to the annual capacity of a port terminal with 10 to 30 shipments per year.
Did you know?
While hydrogen as an RFNBO holds considerable promise, it encounters notable technical and economic challenges. LH2 stands out as the most compact format, but it must be stored at temperatures below -252.8°C. This cooling demand results in a significant energy expenditure, with approximately 30% to 40% of the stored energy consumed during the liquefaction process.
Notably, ammonia exhibits a hydrogen density of 122.4 kg/m3, exceeding that of liquid hydrogen at 71.4 kg/m3. This surprising characteristic and its ease of handling close-to-environmental conditions, position it as a compelling alternative for hydrogen storage.
In more detail, Figure 6 exhibits the composition of the Levelized Cost of Transport for the three shipping alternatives (LH2, NH3, and LOCH). Based on this chart, it is possible to understand that LH2 is not competitive for this application; and that ammonia or other LOCH could become the optimal alternative.
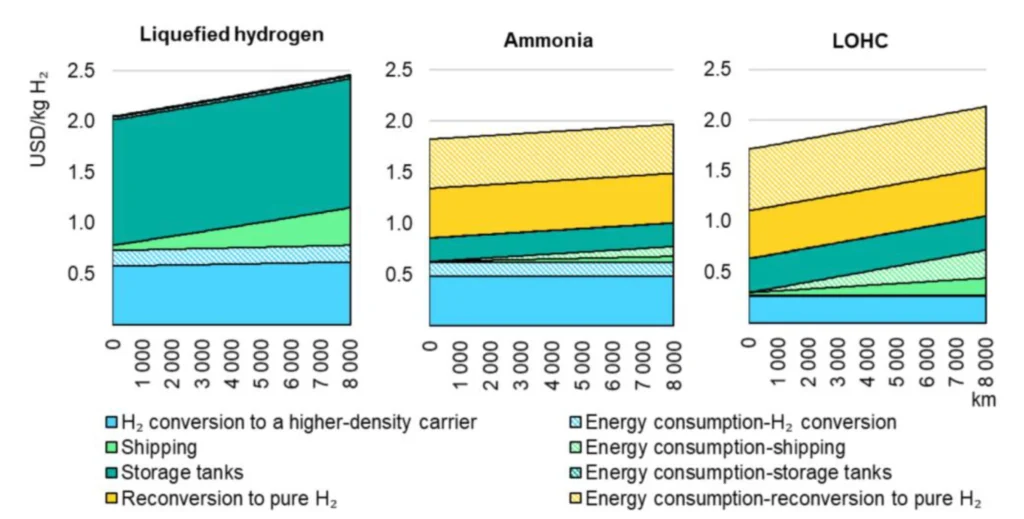
NZE Scenario, 2030.
The cost per stage includes all capital and operational expenditures except those related to energy, which are illustrated separately with a pattern fill.
The discount rate is 5%. It is assumed that import and export terminals handle 20 shipments per year on average.
Ammonia as a direct e-Fuel
Another potential use for ammonia is as a direct fuel for transportation or in industrial heating processes. While this could lead to operational savings by bypassing the need to convert ammonia into hydrogen, it requires the modification of existing large industrial equipment. Currently, some companies are exploring the development of ship engines, electricity generation turbines, and industrial steel ovens to utilize this new e-fuel.
Moreover, ammonia has recently started to gain traction compared to Methanol (CH₃OH) as an alternative fuel. This is primarily due to the abundance of nitrogen in the air (78%) and the relatively low cost of capturing it; in contrast with the expensive process of capturing carbon from the atmosphere (less than 0.5% of air composition), and the scarcity of carbon generation (as CO2) in the future.
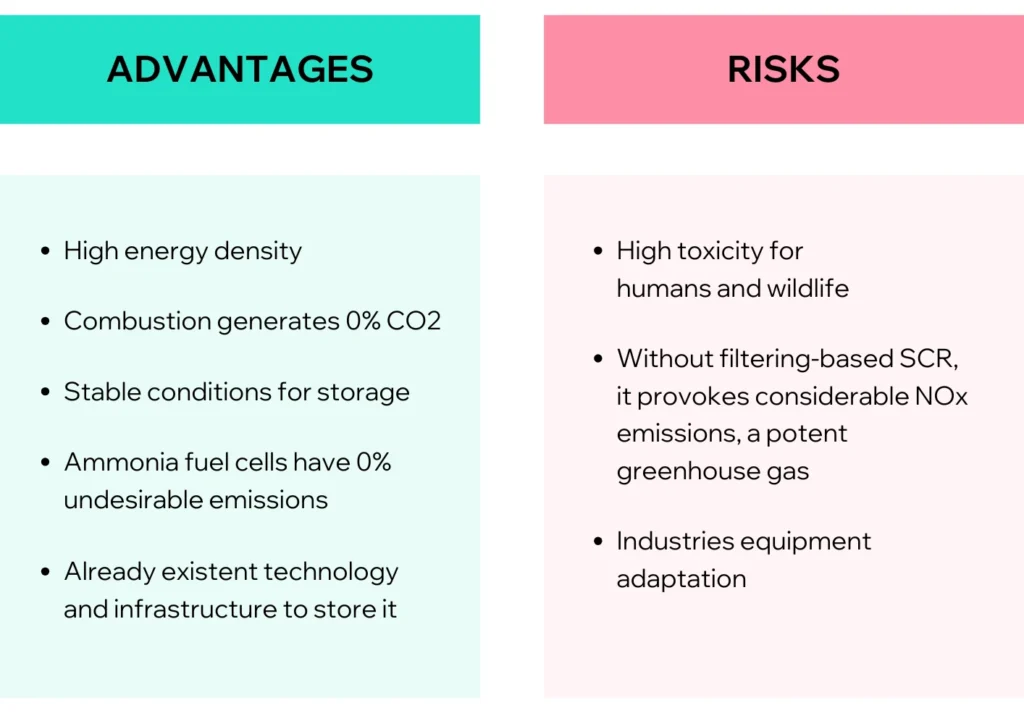
However, there are some challenges related to using ammonia directly as a fuel, since it has been pointed out that improper handling of ammonia can pose hazards to all forms of life. Firstly, it is highly toxic to humans and wildlife, meaning accidental spills could cause immediate harm to both people and the environment. Nonetheless, ammonia has been handled throughout the glove for the past century, with various technologies and protocols in place to ensure safe containment.
Secondly, the combustion of ammonia produces NOx emissions, known as greenhouse gases with an even worse effect than CO2 on the environment. However, NOx gases have long been captured in diesel combustion engines using Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) filters, which can be considered a mature technology.
Regardless of the developing future of this application, much has been discussed about the benefits and risks of using ammonia as a fuel. Table 2 provides a concise comparison of the most significant aspects.
Ammonia’s transformation from an intermediate feedstock in the fossil fuel era to a cornerstone of the renewable future symbolizes the continuous evolution of the energy sector. As we progress towards a more sustainable tomorrow, the potential of renewable ammonia presents a hopeful solution to significant industry challenges.
How to accelerate your project development with Southern Lights
At Southern Lights, we develop software solutions to allow energy developers to do conceptual design, feasibility studies, and optimization of their project portfolio and business model. From origination and greenfield stages to pre- FEED and later stages, Southern Lights offers software with automatized features to derisk and optimize your decision-making and streamline your processes and business development needs in the early stages including conceptual design, LCO-X optimization, feasibility studies and more.
If you want to learn more about the Southern Lights software or would like to integrate Southern Lights into your toolbox and workflow to increase your competitiveness in the market, reach out or book a call with us today.




